Whether it’s because you’re not ready for kids yet or prefer to keep your family small, there are many reasons why a woman may be looking at birth control options in Singapore. Most importantly, it gives us control and freedom over our bodies, without fear of a pregnancy we may not want nor are prepared for.
Not sure which birth control works best for you? Here is a comprehensive guide to what you need to know about birth control options in Singapore.
Contraceptives in Singapore
There are several types of contraceptives:
Hormonal Birth Control works by releasing hormones into the body to prevent ovulation. They typically contain progestin and oestrogen. Examples include:
- Birth Control Pills
- Injections or Implants
- Contraceptive Patches or Rings
- Hormonal Intrauterine Devices (IUD)
Non-Hormonal Birth Control rely on other methods to stop pregnancies. Examples include:
- Condoms which use the barrier method prevent the sperm from meeting an egg in the uterus
- The copper IUD is an alternative to the hormonal IUD
- There are also sterilisation surgeries, such as ligation for women and vasectomy for men, that permanently prevent pregnancy
We’ll break down what each mean in this comprehensive guide to birth control options in Singapore.
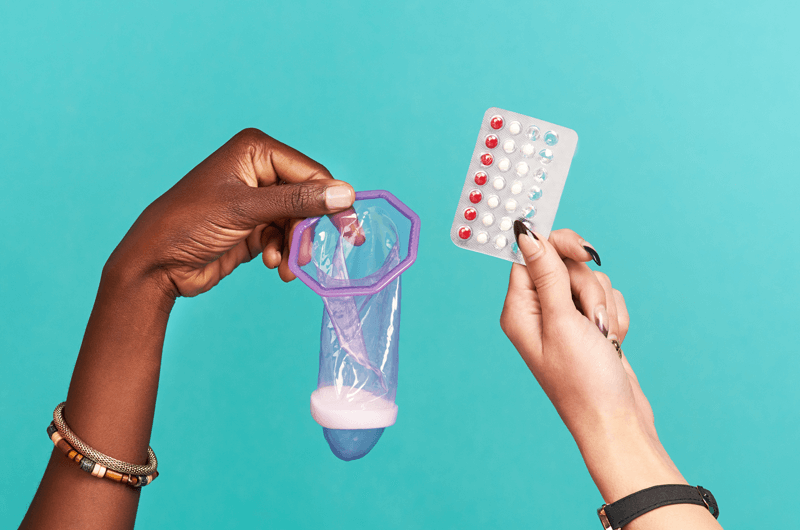
Male Condoms
Male condoms are made of thin latex, polyurethane or polyisoprene. They should be worn when your partner’s penis is erect, and before any sexual contact.
Effectiveness: Male condoms are 98% effective at preventing pregnancies when used correctly.
Pros
- Convenience: Male condoms are easily accessible at supermarkets and convenience stores, and they do not require a doctor’s prescription, unlike many other contraceptives.
- Protection against STIs: Male condoms are one of the few contraceptive methods that also protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Even if you’re using another form of birth control, condoms are recommended, especially when having sex outside of a committed relationship.
Cons
- Risk of failure: Condoms have a higher failure rate compared to some other contraceptive methods. This effectiveness depends on proper use, including how well they are worn. There’s also the risk of the condom tearing or slipping during intercourse, which can compromise protection.
Price: Depending on the brand you purchase, you can get condoms for as low as $4.35 for a packet of three.
Birth Control Pills
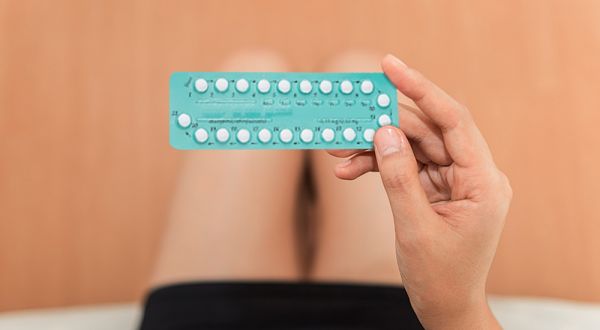
Commonly referred to as “the pill”, birth control pills release hormones that prevent ovulation and create conditions in your body that make it difficult for an egg to be fertilised.
Typically, you take a pill every day for 21 consecutive days, followed by a 7-day break. You can begin your pill regimen on any day, but it’s crucial to take it consistently—ideally at the same time each day—to maintain effectiveness.
Effectiveness:
When used correctly, birth control pills are up to 99% effective at preventing pregnancy.
Pros
- Convenient: Simply take one pill daily. Set a reminder on your phone to ensure you never forget!
- Regulates periods: Even women who aren’t sexually active can benefit from the pill. It helps lighten periods, reduces menstrual cramps, and can even improve hormonal acne.
- Reversible: Fertility typically returns quickly after stopping the pill.
Cons
- Requires consistency: Missing a single day can reduce effectiveness.
- Potential side effects: Some women may side effects such as headaches, mood swings, weight gain, or bloating while taking the pill. If this occurs, consult your doctor about adjusting the dosage or switching brands.
- Women over 35 who smoke should avoid the pill, as it may increase the risk of stroke or heart attack. Always consult your doctor to find the right contraceptive for your needs.
Price: Birth control pills are available through the Doctor Anywhere app starting at $45, with a doctor’s prescription.
Contraceptive Patch and Rings
Both contraceptive patches and rings work by releasing hormones through your skin or vaginal lining into your bloodstream, preventing pregnancy. Like the pill, these methods follow a 3-week-on, 1-week-off cycle.
- Contraceptive patch: The patch is worn on your skin—anywhere that’s clean and dry. Apply a new patch weekly for three weeks, then go patch-free during the fourth week. To avoid irritation, rotate the application site each week.
- Contraceptive ring: A soft, flexible ring that you insert into your vagina for three weeks and remove during the fourth week. After the ring-free week, insert a new one to begin the cycle again.
Effectiveness: Both methods are 91% to 99% effective at preventing pregnancy.
Pros
- Convenient: These methods are easier to maintain than daily pills, with patches needing replacement once a week and rings once every four weeks. The patch is durable and stays on during showers and physical activity.
- Helps to regulate periods: Like the pill, these methods can help lighten periods and reduce menstrual cramps.
- Reversible: Fertility typically returns quickly after discontinuing use.
Cons
- Possible side effects: Some women experience nausea, headaches, tender breasts, or even bleeding during periods. The contraceptive ring may also cause vaginal discomfort for some users.
Price:The patch typically costs $36–50 per month, while the ring may cost around $60 per month.
Contraceptive Implant

A contraceptive implant is a small, flexible plastic rod inserted under the skin of your upper arm by a doctor. The procedure takes less than 10 minutes and is performed under local anaesthesia for minimal discomfort.
The implant releases a low dose of the hormone progestin, which prevents pregnancy. Once in place, it provides protection for up to three years without needing replacement.
Effectiveness: Implants are up to 99% effective at preventing pregnancy.
Pros
- Long-lasting and reliable: Ideal for women who prefer not to think about daily or monthly birth control. It’s convenient and effective for up to three years.
- Oestrogen-free option: Women sensitive to oestrogen can opt for the implant, as it only contains progestin.
- Reversible: Fertility returns quickly after the implant is removed.
Cons
- Possible scarring:As the implant is inserted under the skin, minor scarring may occur.
- Side effects: Some women may experience weight gain, headaches, tender breasts, nausea, and irregular bleeding, though these effects often subside after a few months.
Price: Implants typically cost between $400–600, providing protection for up to three years.
Birth Control Injection
The birth control injection, containing the hormone progestin, is administered by your doctor every 12 weeks to prevent ovulation. This means you’ll need about four injections per year for continuous protection.
Effectiveness: When administered regularly, the injection is up to 98% effective.
Pros
- Convenient and non-invasive: A great option for women who prefer a long-lasting method without the need for daily or weekly routines. It’s also ideal for those who don’t want to use an implant or IUD.
- Less frequent dosing: With just four injections a year, it’s a convenient solution for birth control.
Cons
- Delayed return to fertility: After stopping injections, it may take six to 12 months for your fertility to return. Keep this in mind if you’re planning to conceive in the near future.
- Side effects: Common side effects include weight gain, headaches, tender breasts, nausea, and irregular bleeding, which may persist during the first six to 12 months of use.
Price: Each injection typically costs between $150–200.
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
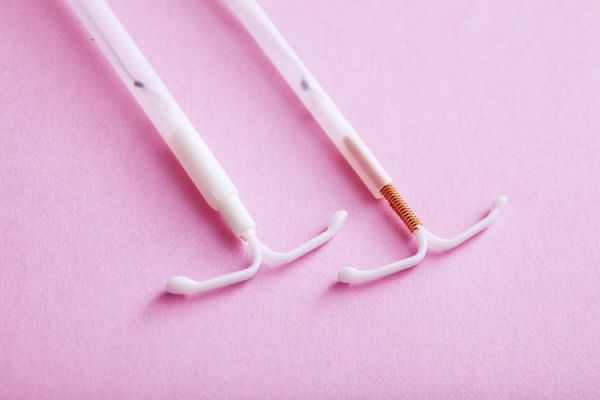
An IUD is a small, T-shaped device that a doctor inserts into your uterus. It provides long-term birth control without the need for daily or monthly maintenance, lasting up to five years.
There are two types of IUDs:
- Copper IUD: Prevents pregnancy by releasing copper ions that are toxic to sperm, stopping them from reaching the egg.
- Hormonal IUD: Releases hormones to prevent pregnancy by thickening cervical mucus and thinning the uterine lining.
Effectiveness: IUDs are 99% effective.
Pros
- Long-lasting and reliable: IUDs are ideal for women seeking a long-term, hassle-free contraceptive option. Once inserted, they can last up to five years.
- Immediate effect: Copper IUDs start working right away, while hormonal IUDs take a few days.
- Reversible: Fertility returns quickly after the IUD is removed.
Cons
- Insertion discomfort: Some women may experience cramping or pain during insertion, but the discomfort usually lasts only a few minutes. Pain relief medication can be taken beforehand to ease anxiety.
- Risk of infection: There is a small risk of pelvic infection within the first 20 days of insertion due to bacteria entering the uterus.
- Side effects: Common side effects include headaches, breast tenderness, and irregular bleeding, which usually improve after the first six months.
Price: An IUD costs $400 – 500 and can last for up to five years.
Sterilisation Surgery
Sterilisation is a permanent birth control solution for individuals or couples who are certain they do not want children in the future. This procedure is called a vasectomy for men and tubal ligation for women.
- Vasectomy: A straightforward procedure where the tubes that carry sperm in a man’s scrotum are sealed, preventing sperm from mixing with semen. It does not affect a man’s ability to maintain an erection or have sex.
- Tubal ligation: Commonly known as “having your tubes tied,” this procedure involves clipping or sealing a woman’s fallopian tubes to prevent sperm from reaching the egg. It is more complex than a vasectomy.
Effectiveness: Both methods are close to 100% effective.
Pros
- Permanent and reliable: Ideal for those certain they do not want children, sterilisation provides long-term peace of mind without the need for ongoing birth control.
- No impact on hormones: Unlike hormonal contraceptives, sterilisation does not affect hormone levels, meaning no side effects like weight gain, headaches, or changes to menstrual cycles.
Cons
- Not reversible: Reversing sterilisation is difficult and not always successful. It’s important to be fully confident in your decision before undergoing surgery.
- Risk of complications: As with any surgery, there are small risks of complications such as infection, but these are generally minor and treatable with rest and antibiotics.
Price: The cost of sterilisation varies depending on whether the procedure is done in a public or private hospital.
- Vasectomy:
- Public hospital: Starting from $200
- Private hospital: Starting from $2,000
- Tubal ligation:
- Public hospital: Starting from $1,000
- Private hospital: Starting from $10,000
Emergency Contraceptive Pills
Commonly referred to as the “morning after pill,” emergency contraceptives are designed for use after unprotected sex or contraceptive failure, such as a condom slipping or breaking. These pills are not intended for regular birth control use and should only be taken in emergencies.
For maximum effectiveness, it’s important to take the pill as soon as possible, ideally within 24 hours. The pill works by delaying or preventing ovulation, but it cannot reverse a pregnancy.
Effectiveness: The earlier it’s taken, the more effective it is. Emergency contraceptive pills are 75%–89% effective if taken within 3 days of unprotected sex.
Pros
- Convenient for emergencies: The morning after pill offers a quick solution in unexpected situations. You can visit a GP to get a prescription and purchase it when needed.
Cons
- Mental stress: Taking the morning after pill can be emotionally taxing, as it’s often used after something has gone wrong. Using a regular birth control method may reduce the need for emergency options and the stress that comes with them.
- Side effects: Common side effects include headaches, abdominal pain, fatigue, and disruptions to your menstrual cycle.
Price: Emergency contraceptive pills are available through the Doctor Anywhere app for $45, with a doctor’s prescription.
In summary, there are various birth control options available to you in Singapore. Each has its pros and cons. Pick the one that is most suitable for your lifestyle and health conditions.
Other Birth Control Methods
In addition to the contraceptives mentioned above, there are alternative methods that some couples use to prevent pregnancy. However, these are generally less reliable than medically approved contraceptives.
Counting Ovulation Days
A woman can only get pregnant on a few days during her menstrual cycle. This ‘fertile window’ occurs when ovulation happens.
Typically, ovulation happens 14 days before the onset of your period. As such, you would need to track a typical menstrual cycle by counting the number of days between when your periods start. Your most fertile days are the three days leading up to and including the day of ovulation. These are the days you should avoid having sex on if you don’t want to get pregnant.
As the math may be tricky, it could be easier to download a period-tracking app, such as Clue, that will do this scheduling for you.
Withdrawal
The withdrawal method—also known as “pulling out”—involves withdrawing the penis from the vagina before ejaculation to prevent pregnancy. Some couples opt for this method as an alternative to other contraceptives, but it’s not highly effective in preventing pregnancies.
Timing withdrawal can be difficult, and even if executed correctly, sperm may still be present in pre-ejaculate. Additionally, since this method involves unprotected sex, it increases the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
As you can see, various birth control options are available. Whatever method you choose, remember to use condoms if you’re not in a committed relationship, as they offer protection against STIs.
Speak to a doctor to better understand the birth control method that suits you best. Our doctors are available 24/7 to provide non-judgmental advice. You can also purchase birth control pills and emergency contraceptive pills from Marketplace on the Doctor Anywhere app with our doctor’s prescription.