Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that is endemic in Singapore. According to the Ministry of Health, the majority of TB cases are either male or older individuals. While TB had once been fatal, infected individuals are now able to recover completely by detecting TB early and finishing their full course of medication. If you think you are experiencing symptoms of TB.
SPEAK TO A DOCTOR NOWSPEAK TO A DOCTOR NOW
What is tuberculosis?
TB is an infectious disease caused by a germ called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It commonly affects the lungs, although may also impact any other tissue or organ in the body.
There are two types of TB infection:
- Latent TB infection: A latent infection occurs when an individual’s immune system is able to fight off the tuberculosis germs and prevent them from growing. While the germs are still alive in their body, they are rendered inactive. As such, someone with a latent TB infection may not experience any symptoms and would not be able to spread TB to others.
- Active TB infection: An active infection typically occurs in individuals with a weaker immune system. Individuals with an active TB infection would experience symptoms and can also spread the disease to others.
The risk of an active TB infection is higher for individuals:
- with underlying medical conditions such as HIV infection and diabetes;
- who have a weakened immune system e.g. due to drugs or sickness;
- who have poor nutritional status; and
- are substance abusers/drug addicts.
How does tuberculosis spread?
TB is an air-borne disease that spreads through the respiratory droplets of an infected individual. For example, if someone with TB coughs or sneezes and the people around them breathe in these bacteria-containing droplets, they may be infected with TB.
Conversely, TB is NOT spread by:
- shaking someone’s hand
- sharing food or drink
- touching bed linens or toilet seats
- sharing toothbrushes
- kissing
What are the symptoms of tuberculosis?
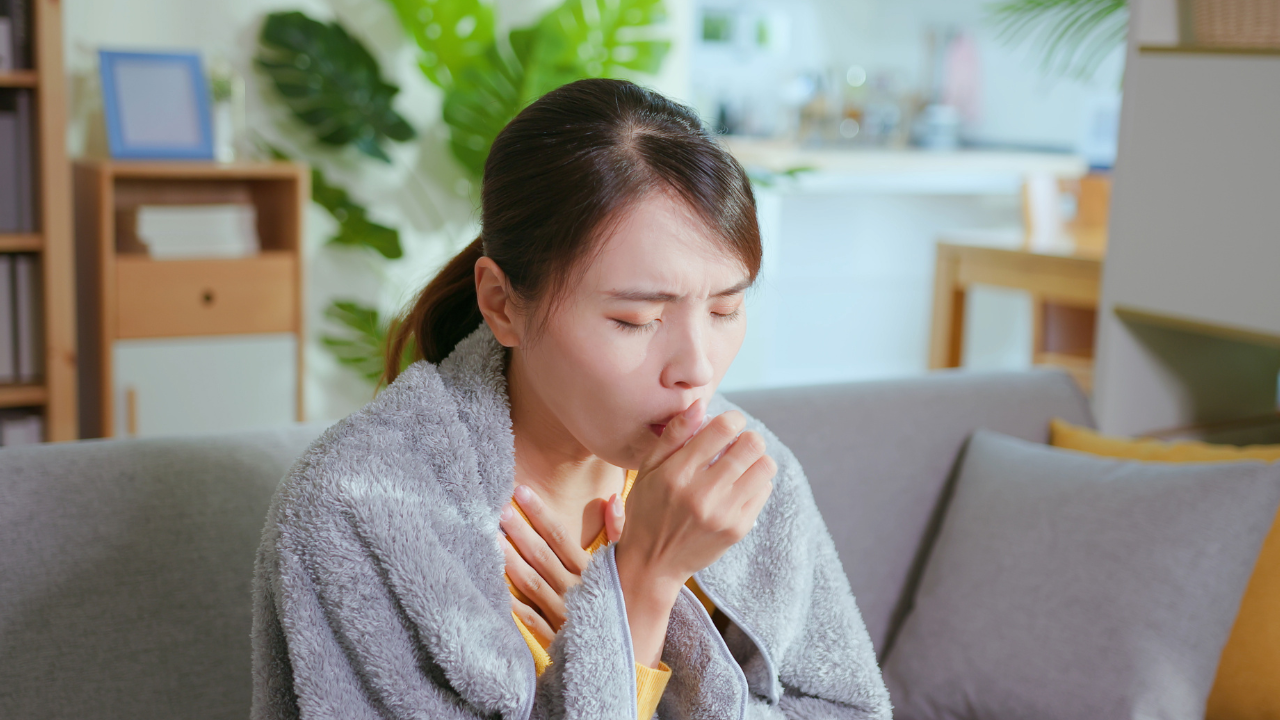
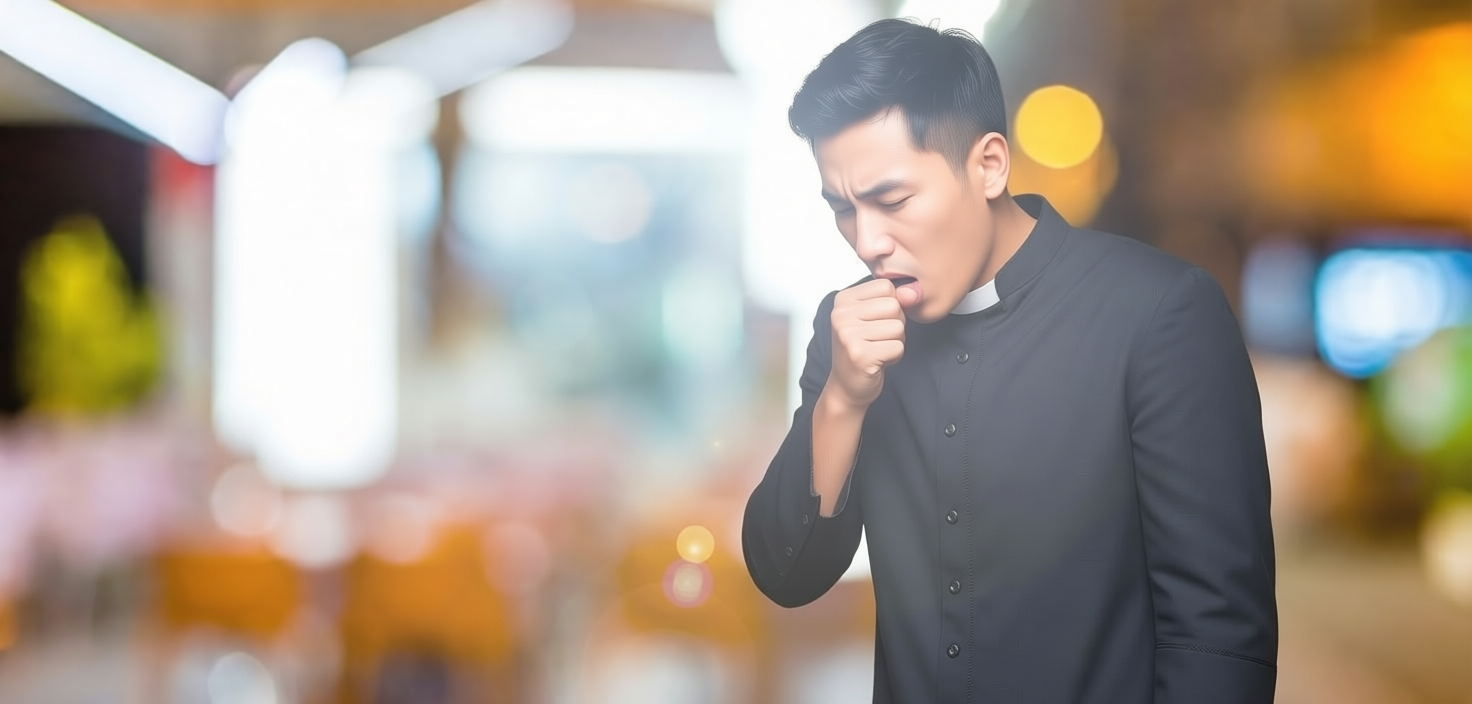
The most telling symptom of TB is a persistent cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer.
Other common TB symptoms include:
- Low-grade fever
- Night sweats
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood or sputum
If you are experiencing these symptoms over a prolonged period, you should speak to a doctor immediately for medical advice.
How is tuberculosis treated?
TB can be cured with anti-TB drugs. Typically, a full course of medication may last 6 – 9 months and consists of several types of drugs.
More than 95% of individuals with active TB are cured if they finish their medications. What is most important for a full recovery is to stay on your medication and complete the entire course, even if your symptoms are gone. This is to prevent your TB from recurring or for the infection to become resistant to the drugs.
Drug-resistant TB is extremely difficult to treat as less effective drugs will have to be used. In such situations, you will need to take medication for a longer period in order to clear the infection.
When should you see a doctor for tuberculosis?
Early detection and treatment is key to managing TB. If you have a persistent cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer, or have any of the other symptoms above, you should speak to a doctor as soon as possible.
You will need to take a chest x-ray, and possibly other tests, for an accurate diagnosis of TB. Your doctor will be able to advise you on the proper procedures, during your consultation.
Worried about TB symptoms? We’re here to support you.
SPEAK TO A DOCTOR NOWSPEAK TO A DOCTOR NOW
with medication delivered to you within 3 hours.