Inflammation is your body’s immune system response to protect and heal you from infection, injury, or disease. However, it is important to make a distinction between 2 types of inflammation.
Types of Inflammation
Acute Inflammation
The swelling that you experience when you twist an ankle or sprain your wrist is an example of acute inflammation. It becomes red and signals to you not to put weight or further aggravate the injury. This is your body’s natural response to injury and part of the healing process. Acute inflammation can also occur internally as in the case of appendicitis and sore throats. The symptoms are temporary and will dissipate as the injury heals.
Chronic Inflammation
This is referred to as long-term inflammation which can last for several months to years. When inflammation goes on for this long, the immune system works overtime, continually pumping white blood cells which mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs. This type of inflammation is like a fire that is raging out of control and does more harm than good.
Research has shown that chronic inflammation is associated with diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. There are various things that can trigger long-term inflammation including diet, lack of sleep, or genetics.
Signs of Chronic inflammation
Digestive issues
While we have the occasional bout of diarrhoea or gassiness, a persistent problem with the gut could be a sign of chronic inflammation. Inflammation in the gut can lead to bloating, loose stools and cramping. Chronic inflammation throughout the body can also contribute to a higher intestinal permeability where bacteria and toxins get through the intestinal wall into the rest of the body when it is not supposed to.
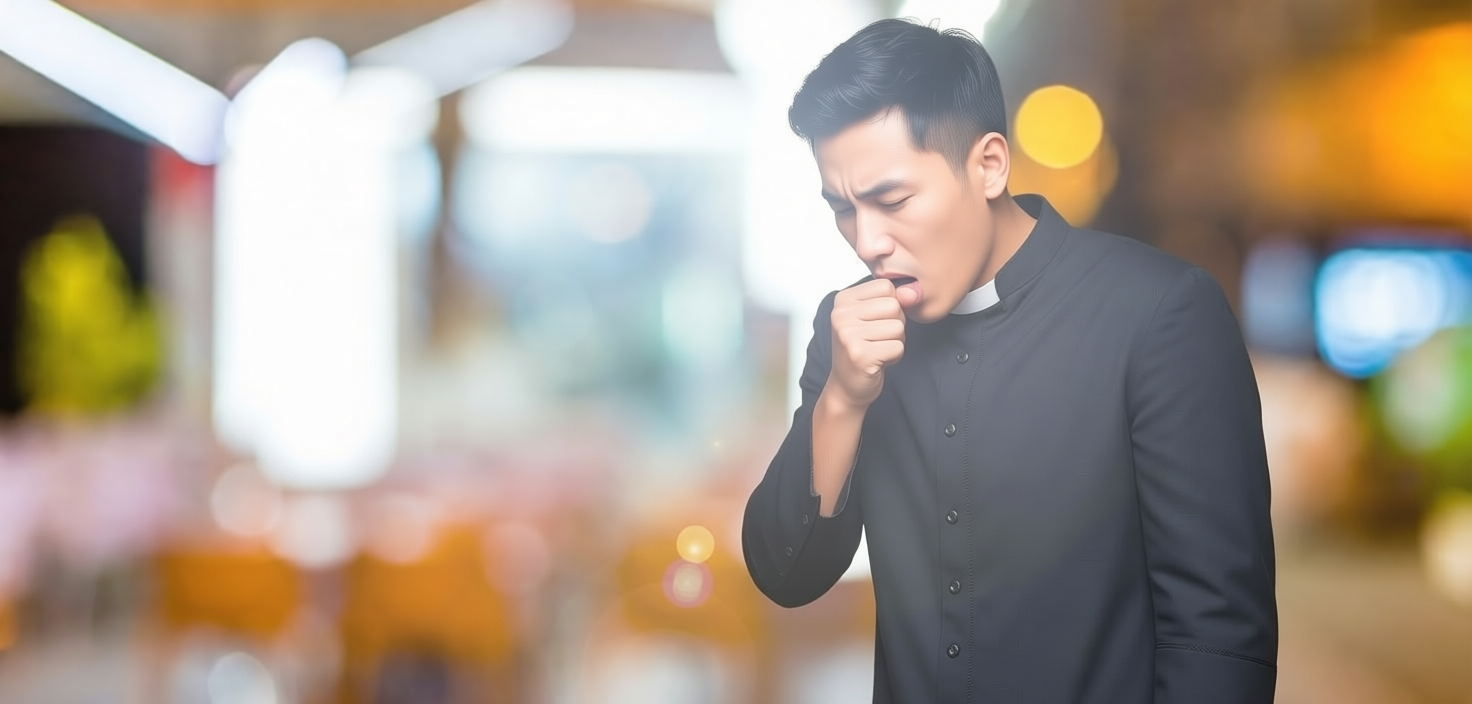
Excessive mucus
If you have a constant need to clear your throat or blow your nose, it probably points to excessive mucus production. When inflamed, thick phlegm is produced to protect the cells in the lining of the respiratory system.
Constant fatigue and brain fog
Inflammation can also affect you physically and mentally. Physically, you could feel constantly fatigued despite getting adequate sleep. This is a sign that your immune system is working overtime to fend off chronic inflammation. Mentally, signs could be subtle, such as forgetting where you put an item frequently, or be severe, like forgetting what you are saying halfway through a sentence.
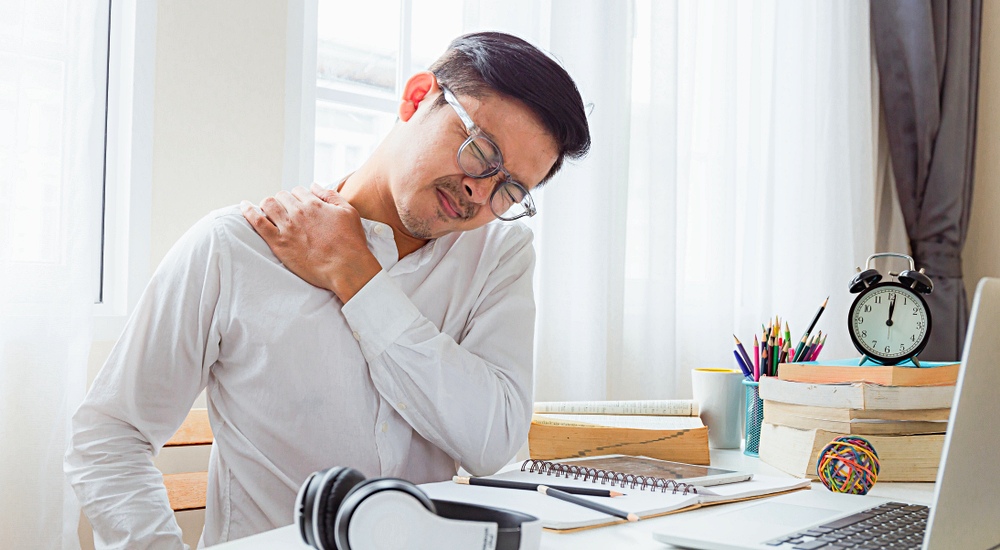
Body aches and pains
Experiencing pain on a regular basis that is not associated with any injury could be an indicator of inflammation. It could also be rheumatoid arthritis where your immune system, while working overtime, mistakenly attacks cartilage and bone within the joints. Do not brush off this pain as a result of old age.
Skin breakouts
People with internal inflammation often suffer from eczema, acne breakouts or dry skin. This is the body’s way of showing that something is not right internally.
Speak to someone knowledgeable
These symptoms when viewed as individual occurrences on a day to day basis may not seem like a big deal, but if it is recurring and there are no attributable factors (e.g. pain but with no injury, mucus but with no allergens) could point to chronic inflammation. While you can try to alleviate the pain with some lifestyle changes, seeking professional medical advice is the best option.
If left untreated, chronic inflammation may lead to illnesses including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, arthritis and bowel diseases. Speak to your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms that has been lingering.